Birth of the cool: a two-centuries decline in emotional expression in Anglophone fiction
Jun 4, 2017· ·
0 min read
·
0 min read
Olivier Morin
Alberto Acerbi
Abstract
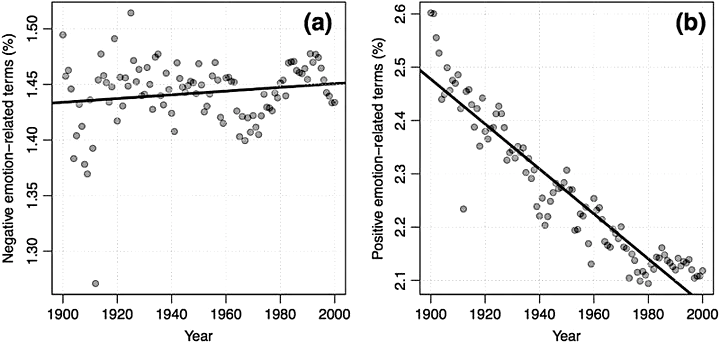
The presence of emotional words and content in stories has been shown to enhance a story’s memorability, and its cultural success. Yet, recent cultural trends run in the opposite direction. Using the Google Books corpus, coupled with two metadata-rich corpora of Anglophone fiction books, we show a decrease in emotionality in English-speaking literature starting plausibly in the nineteenth century. We show that this decrease cannot be explained by changes unrelated to emotionality (such as demographic dynamics concerning age or gender balance, changes in vocabulary richness, or changes in the prevalence of literary genres), and that, in our three corpora, the decrease is driven almost entirely by a decline in the proportion of positive emotion-related words, while the frequency of negative emotion-related words shows little if any decline. Consistently with previous studies, we also find a link between ageing and negative emotionality at the individual level.
Type
Publication
Morin, O., Acerbi, A. (2017), Birth of the Cool. A two-centuries decline in emotional expression in Anglophone fiction, Cognition and Emotion, 31 (8), 1663-1675